What is Hand Hygiene?
Hand Hygiene means cleaning your hands by using either handwashing (washing hands with soap and water), antiseptic hand wash, antiseptic hand rub (i.e. alcohol-based hand sanitizer including foam or gel), or surgical hand antisepsis.

Why Practice Hand Hygiene?
Cleaning your hands reduces:
- The spread of potentially deadly germs to patients
- The risk of healthcare provider colonization or infection caused by germs acquired from the patient
Two Methods for Hand Hygiene: Alcohol-Based Hand Sanitizer vs. Washing with Soap and Water
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizers are the most effective products for reducing the number of germs on the hands of healthcare providers.
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizers are the preferred method for cleaning your hands in most clinical situations.
- Wash your hands with soap and water whenever they are visibly dirty, before eating, and after using the restroom.
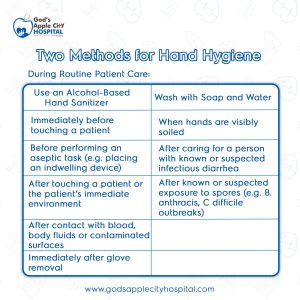
During Routine Patient Care:
Use an Alcohol-Based Hand Sanitizer
- Immediately before touching a patient
- Before performing an aseptic task (e.g., placing an indwelling device) or handling invasive medical devices
- Before moving from work on a soiled body site to a clean body site on the same patient
- After touching a patient or the patient’s immediate environment
- After contact with blood, body fluids or contaminated surfaces
- Immediately after glove removal
Wash with Soap and Water
- When hands are visibly soiled
- After caring for a person with known or suspected infectious diarrhea
- After known or suspected exposure to spores (e.g. B. anthracis, C difficile outbreaks)
Techniques for Using Alcohol Based Hand Sanitizer
- Put product on hands and rub hands together
- Cover all surfaces until hands feel dry
- This should take around 20 seconds
Techniques for washing Hands with Soap and Water
- When cleaning your hands with soap and water, wet your hands first with water, apply the amount of product recommended by the manufacturer to your hands, and rub your hands together vigorously for at least 15 seconds, covering all surfaces of the hands and fingers.
- Rinse your hands with water and use disposable towels to dry. Use towel to turn off the faucet.
- Avoid using hot water, to prevent drying of skin.
- Other entities have recommended that cleaning your hands with soap and water should take around 20 seconds.
- Either time is acceptable. The focus should be on cleaning your hands at the right times.

Methods to Maintain Hand Skin Health
- Lotions and creams can prevent and decrease skin dryness that happens from cleaning your hands
- Use only hand lotions approved by your healthcare facility because they won’t interfere with hand sanitizing products
Fingernail Care and Jewelry
- Germs can live under artificial fingernails both before and after using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer and handwashing
- It is recommended that healthcare providers do not wear artificial fingernails or extensions when having direct contact with patients at high risk (e.g., those in intensive-care units or operating rooms)
- Keep natural nail tips less than ¼ inch long
- Some studies have shown that skin underneath rings contains more germs than comparable areas of skin on fingers without rings
- Further studies are needed to determine if wearing rings results in an increased spread of potentially deadly germs
Kindly Check us out on
Facebook @ godsapple.hospital
Instagram @ godsapplecityhospital

